Ab. http://how to spoken English. How to Learn English
HOW TO LEARN ENGLISH
There are some Rule whose fallow them.If you are want to speak English in a easy way.
THERE ARE FEW METHOD TO SPOKEN ENGLISH.
- To improve spoken English-talk to your self.
- Focus more on fluency than grammar.
- Think in English, speak and record your voice
- Read good books.
- For enjoying purpose watch English movies .
HOW TO ENHANCE SPOKEN ENGLISH SKILLS.

- Speaking regularly in English.
- You should improve Grammar.
- Listening and reading everyday.
- Recording your voices to analyse fluency .
- Read and understand about whole sentence.
- Sings along in English songs .

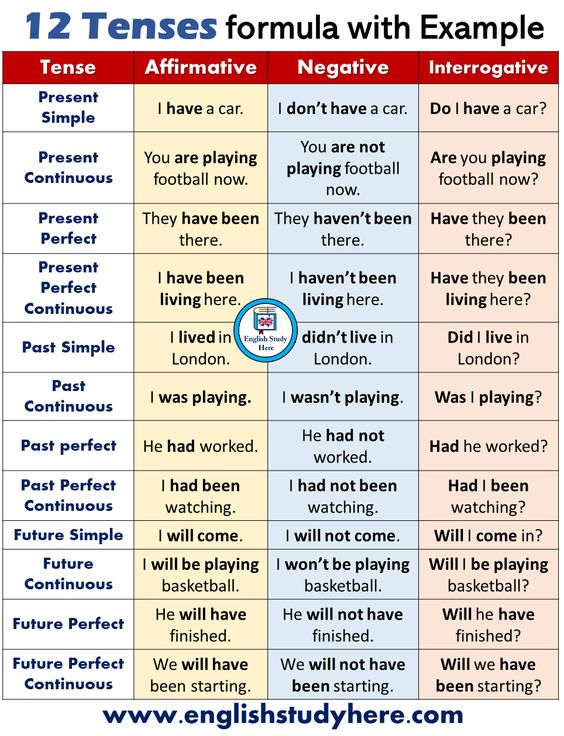
RULE FOR TENSES
Present Tense
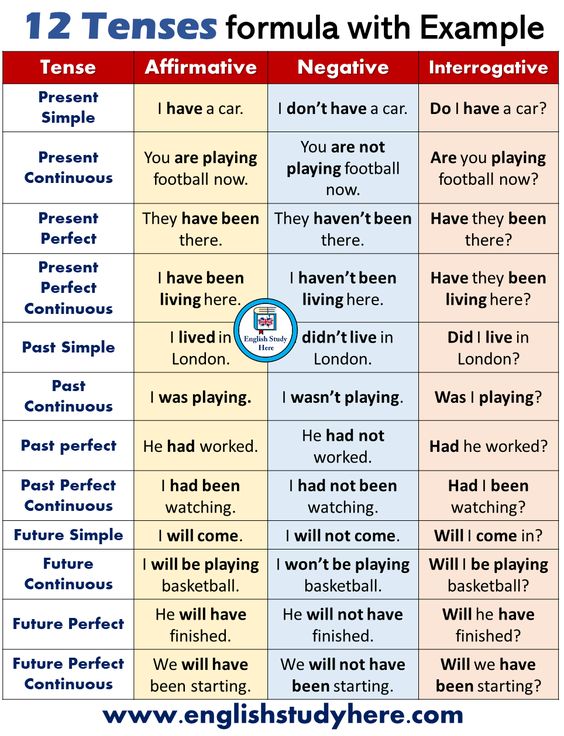
Present Tense can be defined as an expression for an activity that is currently in action or is habitually performed. It is used for a state that generally exists or is currently ongoing.
- Simple Present
Simple Present TenseSingularPluralRule: Subject + V1 + s/es + ObjectRule: Subject + V1 + ObjectExample: The girl sings a song
Here the subject is Girl (singular) and “s” has been added to the verb (sing), followed by the object (song)Example: The girls sing a song
Here the subject is Girls (plural) and no changes have been made with V1 (first form of verb) and the object
- Present Continuous
Present Continuous TenseRule: Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + objectExample: She is eating food
Here the subject is She, followed by “is”
The first form of verb (V1) here is “eat” and “ing” has been added to it, followed by the object “food”
- Present Perfect
Present Perfect TenseSingularPluralRule: Subject + has + V3 + ObjectRule: Subject + have + V3 + ObjectExample: He has cleaned the utensils
Here, “He” is the subject + has
“Cleaned” is the third form of verb and utensils is the objectExample: They have cleaned the utensils
Here, “They” is the subject + have
“Cleaned” is the third form of verb and utensils is the object
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous TenseSingularPluralRule: Subject + has been + V1 + ing + ObjectRule: Subject + have been + V1 + ing + ObjectExample: She has been practising since morning
Here “She” is the subject + has been, followed by “ing” added to the the first form of verb “practise” and then the objectExample: They have been practising since morning
Here “They” is the subject + have been, followed by “ing” added to the the first form of verb “practise” and then the object
Given below are a few examples that may help you differentiate between the four sub parts of present tense easily:
- Raj speaks German (Simple Present for Singular)
- They speak German (Simple Present for Plural)
- She is speaking German (Present Continuous)
- He has learnt German (Present Perfect for Singular)
- They have learnt German (Present Perfect for Plural)
- She has been learning German (Present Perfect Continuous for Singular)
- They have been learning German (Present Perfect Continuous for Plural)
Past Tense
Any event or action that took place in the past can be referred to as the past tense. Below we have discussed in detail the four sub parts of past tense in English grammar.
- Simple Past
Simple Past TenseRule: Subject + V2 + ObjectFor example: He ran away
Here, the subject is “He” and “ran” is the second form of verb (V2) of “run” followed by the object
- Past Continuous
Past Continuous TenseSingularPluralRule: Subject + was + V1 + ing + ObjectRule: Subject + were + V1 + ing + ObjectFor example: She was going shopping
Here, the subject is “She” + was
It is followed by the first form of verb (V1) “go” + “ing” and then the object “shopping”For example: They were going shopping
Here, the subject is “They” + were
Followed by the first form of verb (V1) “go” + “ing” and then the object “shopping”
- Past Perfect
Past Perfect TenseRule: Subject + had + V3 + ObjectFor example: Sumit had left the job
Here the subject is “Sumit” + had
Then “left”, which is the third form of verb (V3) “leave” is given followed by the object
- Past Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous TenseRule: Subject + had been + V1 + ing + ObjectFor example: They had been preparing for their performance for two months
Here the subject is “They” + had been
It is followed by “preparing”, which is the first form of verb (V1) of “prepare” and then the object
To help you understand past tense and its form even better, given below are a few examples to simply the concept:
- I played football yesterday (Simple Past)
- I was playing football yesterday (Past Continuous for Singular)
- They were playing football yesterday (Past Continuous for Plural)
- They had played football yesterday (Past Perfect)
- They had been playing football the entire yesterday (Past Perfect Continuous)
Given below are a few articles to clarify the confusion between various common but confusing words in the English Language. It is vital aspirants gain clarity on the basic concepts to ace this section, as they are very well aware that English is an important part of the syllabus of various competitive exams.Difference Between Affect and EffectDifference Between Center and CentreDifference Between Principal and PrincipleDifference Between Program and Programme
More such concept-wise, subject-wise differences can be found on the 100 Difference between Articles page linked here.
Future Tense
The actions that are to take place in the future fall in the category of the future tense. We have discussed the subparts of the future tense in detail further below in the article, followed by the examples for the same.
- Simple Future
Simple Future TenseRule: Subject + will/shall + V1 + ObjectFor Example: I will visit my Uncle tomorrow
Here, the subject is “I” + will
It is followed by the first form of verb (V1) “visit” and then the object
- Future Continuous
Future Continuous TenseRule: Subject + will be/shall be + V1 + ing + ObjectFor Example: I shall be going to the market tomorrow
In this example, the subject is “I” + shall be
Following it is the first form of verb (V1) “go”+ing and then the object
- Future Perfect
Future Perfect TenseRule: Subject + will have/shall have + V3 + ObjectFor Example: I shall have prepared the notes by tomorrow morning
In this example, the subject is “I” + shall have
It is followed by “prepared”, which is the third form of Verb (V3) “prepare” and then the object
- Future Perfect Continuous
Future Perfect Continuous TenseRule: Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + ObjectFor Example: She will have been working here since 2015
Here, the subject is “She” + will have been
It is followed by the first form of verb “work”+ing and then the object
Given below are a few examples that may help you clarify the future tense concept clearly:
- She will go to school tomorrow (Simple Future)
- She will be going to school tomorrow (Future Continuous)
- She will have gone to school tomorrow (Future Perfect)
- She will have been going to school tomorrow 1(Future Perfect Continuous)
